
PCB Essentials: Definition, Components, and Types Explained
What’s a PCB? A Quick‑and‑Cheery Guide
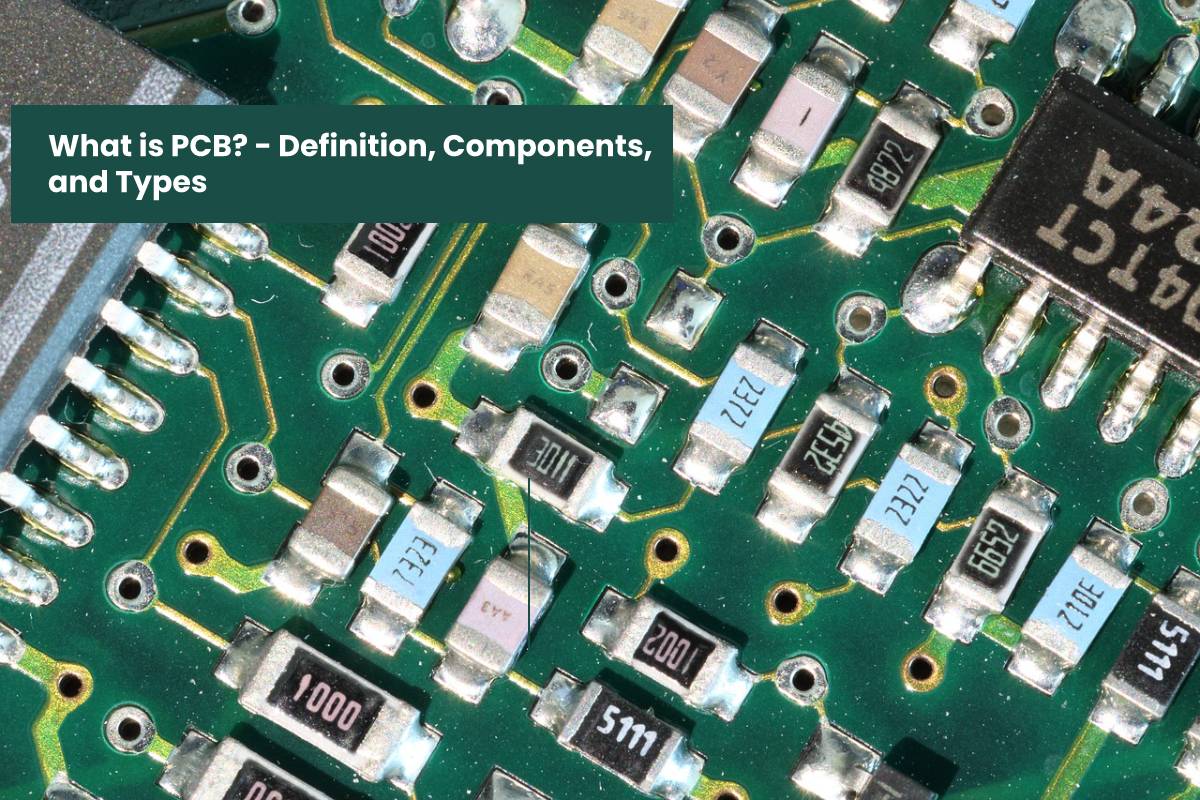
If you’ve ever given a tech gadget a poke or a swipe, you’ve already had a run‑in with a printed circuit board (PCB). That sleek little stack of copper pathways is the backstage crew for phones, laptops, game consoles, and even your pocket‑sized guitar amps.
1. The Basic Pitch – What’s a PCB?
A PCB is basically a supercharged roadmap for electricity. Think of it as a city map where the streets are copper traces that guide electric signals from one component to the next. Without it, your device would just be a pile of random parts wobbling around like a herd of chickens.
2. The Layers – The Vice‑Presidents of the Board
Most PCBs are not just one flat surface; they’re multi‑layered masterpieces. From the outer copper snakes that carry power, through insulating decks that keep everything separated, to the back side that often hosts extra circuitry – layers are where the board’s brain lives.
- Top Layer – The front lines, carrying primary signals.
- Inner Layers – The secret operatives, often used for ground planes or power distribution.
- Bottom Layer – The silent support, sometimes where antennas or extra traces are tucked in.
3. The Building Blocks – Components That Do the Heavy Lifting
Inside the PCB’s framework, a variety of components bring life to the board:
- Resistors – The humble speed bumpers that slow down current.
- Capacitors – The memory cells that hold charge for a blink.
- Integrated Circuits (ICs) – The brainy micro‑processors who do the heavy math.
- Diodes – The one‑way gates that keep charge flowing in the right direction.
4. Types of PCBs – From Simple to Sleek
Depending on the gadget’s ambition and budget, PCBs come in a few flavors:
- Single‑Side – The eggshell of boards for low‑cost gadgets.
- Double‑Layer – Classic, everyday boards that’re cheap and reliable.
- Multilayer – The Swiss army knife of PCBs, used in high‑performance devices like smartphones and GPUs.
- Flexible & Rigid‑Flexible – The stretchy pieces that fit into phones or wearable tech.
5. In a Nutshell – Why PCBs Matter
A PCB is the silent hero that transforms a bowl of disconnected components into a functioning gadget. Without it, your phone would be nothing but a shiny shell, your laptop a garbage‑filled drawer, and your electric guitar would probably just look like a battery holder with a few wires. So, next time you pick up your device and press that power button, remember: behind the scenes is a network of tiny traces doing the real hustle.
That’s it—your crash‑course to becoming a little PCB aficionado. Now, go brag about the board that powers your life!
Definition of a PCB
Why PCBs are the MVPs of Tech
When you think of your shiny laptop or that super‑fast smartphone, you probably think of the screen or the battery. But if you want to get the real star of the show, look under the hood—it’s called a PCB, or Printed Circuit Board.
What the Heck Is a PCB?
Why Your Computer Must Keep Its Cool
The PCB is the lifeline. If water sneaks in, it’s like throwing a chemical storm into a highways system:
Bottom Line
So next time you’re tempted to bring your laptop to the pool, remember: it won’t survive. The PCB is the heart, and even a little drip can sending your gadget off‑beat.
Layers of a PCB
Let’s Talk About PCBs – The Bite‑Sized History
From the one‑layer wonder that once rocked the 1980s to the sophisticated multi‑layer marvels humming inside your smartphone, Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) have come a long, electrifying way.
1⃣ The Base Layer – Substrate
- What it is: The thin board that everything else hangs on. Think of it as the foundation of a skyscraper.
- Most common material: Fiberglass, also marketed as FR4. It’s sturdy, cheap, and loves high temperatures.
- Other options: Some folks go old school with phenolics or keep it classy with glass.
2⃣ The Copper‑Tin Armor
Once the substrate is ready, the next step is to add the copper‑tin foil. It’s laminated under heat and bonded with a clever adhesive, creating the conductive pathways that make your gadgets tick.
3⃣ The Protective Green Shield – Solder Mask
- What it does: Covers the copper, shielding it from accidental shorts and keeping the connections safe.
- Why you know it: It’s that familiar green that you see in every electronics photo.
4⃣ The Final Touch – White Silkscreen Layer
- Visual guide: Labels, logos, and tiny circuit diagrams are printed in white for easy identification.
- Pro tip: Next time you see a white sticker on your phone, there might be a whole story behind it.
So next time you swipe your phone or plug in a charger, remember: a world of layers, materials, and engineering decisions are tucked neatly on that small board – each layer playing its part in the symphony of modern tech.
Components of a PCB
What’s Really Inside a Simple PCB?
Think of a PCB as a tiny electronic orchestra. Even the simplest board plays a symphony of voltage, current, and math—each component gets to do its thing over just the right conditions.
Meet the Superstar Cast
- Transistors – the amplifiers that shout “I’ve got more power!” and boost the charge to louder levels.
- Resistors – the traffic cops that keep the voltage flow in check, like a polite bouncer at a high‑tech club.
- Capacitors – the polite nap‑takers that store a little charge and release it when the board needs a quick burst.
- Inductors – the efficient energy vaults that hold currents for a smooth, wobbly dance.
- Diodes – the one‑way ticket agents that let electrons flow in only one direction, preventing chaos.
- Switches – the robotic directors that control when the flow starts or stops, keeping everything in harmony.
- LEDs (Light‑Emitting Diodes) – the colorful footlights that not only light up the stage but also let current flow only the way they want.
- Batteries – the backstage power crew, supplying the steady voltage our heroes need.
How It All Works Together
Picture this: you’ve got a transistor amplifying the signal, a resistor chopping off any runaway hustle, and a capacitor soaking up the excess to keep the beat steady. Meanwhile, inductors and diodes are escorting the electrons, making sure never a misstep occurs.
In short, each component is a tiny wizard, casting spells of math and physics to create the electronic magic we use every day.
Bottom Line
Even a basic PCB is a carefully choreographed crew—each part doing its solo but harmonizing into a full, working system that powers almost everything in our modern, wired world.
Different Types of PCBs
What’s a PCB, Anyway?
Personas refer to the tiny magic that turns snacks into tech: Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs). The variety is like a wardrobe—each type suits different outfits, from simple gadgets to high‑speed supercomputers.
Single‑Sided PCBs: The “Bare‑Bones” Edition
- Just one copper layer on a single substrate.
- Washing, soldering, and a simple solder mask for protection.
- Cheap, quick to produce – perfect for bulk items or power‑simple circuits.
- Think of a single‑sided board as the family’s basic smartphone (no frills, just go)
Double‑Sided PCBs: The Everyday Star
- Two metal layers, connected via thru‑holes or surface mounting.
- These are the backbone of smartphones, laptops, and amplifiers.
- Need a quick check on your laptop’s temperature? CPU Temp Monitor apps reveal if the board’s staying chill.
Multi‑Layer PCBs: The High‑Speed Typhoon
- Layered with insulators to wrap many copper sheets together.
- Engineers love them for deployin’ massive data‑ highways in complex computers.
- They’re the “a‑maze‑in’” routes that keep signals crisp and fast.
Rigid, Flexible & Hybrid PCBs: The Material Game
Like choosing between a comfy chair or a stretchable yoga mat, your board’s substrate can be:
- Rigid: Straight‑forward, great for organizing components. It’s the “desktop” of society.
- Flexible: Bendable and smart—ideal for environments where temperature swings, or space is tight.
- Hybrid: A mix of both, good for super‑specialized devices.
Manufacturers in this niche build boards that shrug off the heat and stress of rugged conditions while keeping their performance on point.
Takeaway
Whether you’re a DIY hobbyist or a tech giant, understanding the board types let you choose the right fit for your next gadget. And remember: a steady PCB temperature means a happier, longer‑lived device—so keep those temp bools low!
Conclusion
Why PCBs Are the Unsung Heroes of Your Gadgets
Ever wonder what makes your phone stay on, your laptop run smoothly, or that tiny smartwatch still tick‑tocks after a wild adventure? It’s not pretty prints or flashy interfaces—it’s the printed circuit board (PCB) quietly humming in the background.
High‑Frequency PCBs: The Speedsters of the Electromagnetic World
When it comes to high‑frequency signals—think Wi‑Fi, 5G, and radar—those PCBs need to keep the data flowing fast and clean. Engineers design them with tighter copper traces, special dielectric materials, and meticulous layout to avoid unwanted interference.
Aluminum‑Backed PCBs: Heavy‑Darlings for Extreme Temps
Picture a PCB in a space probe or a high‑performance drone: temperatures can shoot into the 100 °C range. To keep the board from wilting, designers sandwich an aluminum plate beneath the PCB. This not only cools the board faster but also gives it a sturdy spine that can survive the test of time—and the occasional launch.
Size, Weight, and Power: The New Era of PCBs
Modern boards are getting lighter and more compact, but the demand for power hasn’t waned. TechCrunch recently spotlighted startups like Tempo Automation that are shaking up the manufacturing scene, helping teams move from hand‑built prototypes to fully streaming mass production.
What’s Hot in PCB Materials?
- Heat‑Resistant Substrates: New polymers and composites that stay stable at higher temps, reducing the need for bulky cooling systems.
- Resilient Coatings: Graphene layers and other thin films that protect against physical wear and tear.
- Eco‑Friendly Options: Bio‑based resins and recyclable designs for the green‑minded engineers.
So the next time you power on your smartwatch, put a smile to the brain that is actually doing the heavy lifting—a compact, resilient, and super‑fast PCB. Without it, your tech would just be a shiny case with nothing inside. PDAs (Print‑Deciding Aware—it’s a thing now, right?) to the future, one board at a time!







