IPsec Unveiled Inside The Tech Protecting Your Connections
Got it! Let’s Dive into IPsec
Security on the internet isn’t just about throwing a firewall at every incoming packet… That would be nice, but a True IPsec solution keeps your data safe in a way that feels almost magical. Below you’ll find a quick walkthrough of the nitty‑gritty and a few chuckles along the way.
1. IPsec 101—What’s the Deal?
- IPsec stands for Internet Protocol Security, a suite of protocols designed to protect IP packets from tampering or snooping.
- Think of it as a bodyguard that watches every packet, making sure no one can peek or walk in without permission.
- It operates at the network layer, meaning it’s not just about TCP/UDP; it’s about every IP packet that’s traveling across the globe.
2. The Low‑down: Major Features of IPsec
- Confidentiality – Encrypts data so only the intended recipient can read it.
- Integrity – Checks that data hasn’t been altered en route.
- Authentication – Confirms the identity of the sending side.
- Replay Protection – Stops old packets from being resent as malicious tricks.
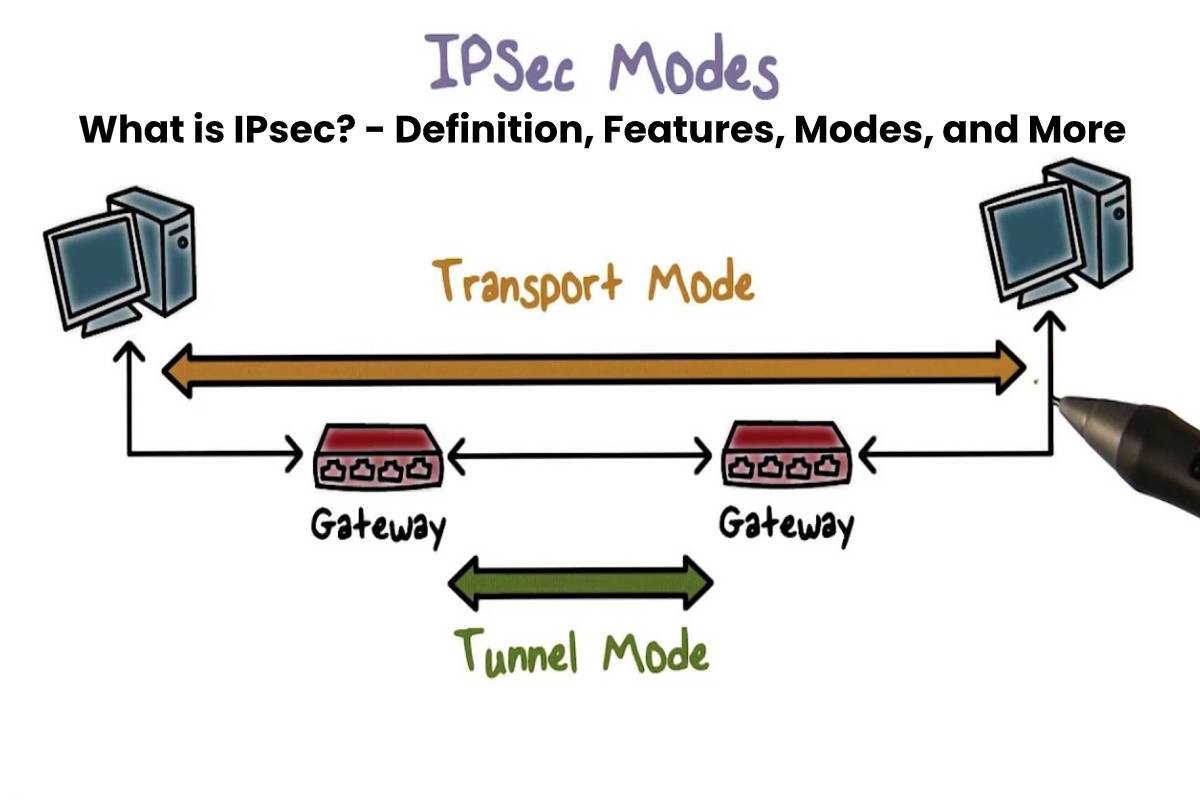
3. Modes of Operation—Transport vs. Tunnel
Transport Mode
Only the payload (the actual data) is encrypted; the original IP header stays untouched. It’s like putting a protective bubble around the meat of your message while keeping the outer shell— the header— visible. Great for end‑to‑end security such as VPN connections between two devices.
Tunnel Mode
Both the header and payload get wrapped up in encryption. The result is a brand‑new IP packet— entirely opaque to eavesdroppers. VPNs between sites or multiple devices usually use tunnel mode because they create a private “tunnel” over public infrastructure.
4. Key Management—Keeping Secrets Safe
- Manual – Key folks type them in, but this is like writing down your password on a sticky note. Tread carefully!
- IKE (Internet Key Exchange) – The modern standard. It automatically negotiates keys, authenticates peers, and handles key rollover.
- Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) – Involves certificates for identity verification, ensuring only trusted parties can hand out keys.
5. NAT and IPsec—the Bumpy Relationship
Network Address Translation (NAT) is awesome for browsers to share a single IP, but it can break IPsec because IPsec relies on unchanged packet headers. Two common solutions:
- NAT‑Traversal (NAT‑T) – Adds extra headers so the packet still slips through NAT.
- Manual Re‑keying or Re-configuration – In some cases, you just have to tweak the setup to avoid the clash.
Final Words
IPsec may sound like a cryptic dance of algorithms, but at its core it’s just ensuring that your data travels safely, quietly, and accurately. Whether you run a personal VPN or a corporate backbone, knowing these fundamentals and a dash of humor can help you navigate the networking seas with ease.
IPsec Definition
IPsec: The Secret Agent of the Internet
Ever wonder how your passwords and online chats stay safe on the wild, open internet? IPsec is the unsung hero that makes that possible.
What’s the Deal?
IPsec (Internet Protocol Security) is a set of add‑on rules that the Internet Protocol (IP) follows. Think of it as the Internet’s personal body‑guard—keeping all your data encrypted and the people who send it verified.
How It Works
- Encryption: Packs your information inside a vault so nobody else can read it.
- Authentication: Confirms who’s talking, so you know you’re chatting with the right party.
- Integrity: Makes sure data hasn’t been tampered with on its way.
Why It’s a Game‑Changer
Without IPsec, transmissions on networks like the Internet would be like throwing letters into a crowded mailbox—easy for anyone to peek at or alter. Thanks to these protocol extensions, you can feel confident that your sensitive info stays private, even on potentially unsafe networks.
Bottom Line
IPsec is the invisible shield that keeps your online life secure. It encrypts your data, verifies your contacts, and guards against malicious snoops—making the internet a safer place, one packet at a time.
What are the main features of IPsec?
IPsec: The Internet’s Unsung Secret‑Keeper
Think of IPsec as the superhero of online communication – it turns ordinary data packets into protected, trustworthy messengers that no one can tamper with or snoop on. Here’s why it’s got everyone’s attention:
1. Interoperability: Fits Right Into the IP World
- You can mix and match it with any IP protocol stack – no plumbing changes needed.
- It speaks the same “language” as routers, firewalls, and even home Wi‑Fi, so it works smoothly everywhere.
2. Data Integrity: “No Peeking! No Spoiling!”
- IPsec tags every packet with a checksum, making sure the data hasn’t been altered on the way.
- If a packet gets corrupted, the entire conversation goes down – better safe than sorry.
3. Cryptographic Protection: Encryption is the Key (and the Lock!)
- It encrypts the contents so that even if someone intercepts the traffic, they’ll see only scrambled gibberish.
- Infinite combinations of keys keep snoops guessing until the target is lit up.
4. Key Management: Batteries That Never Need Recharging
- Supports a variety of key‑exchange methods (IKE, manual, automated), so you can choose what feels safest.
- Keys can be refreshed or revoked on the fly – no more static passwords that age like stale cheese.
5. Authentication: “Who’s Talking to Me?”
- Both endpoints prove their identities, so no impostors or rogue pistols will get in the way.
- Certificates and credentials turn IPsec into a verifiable handshake between devices.
Bottom line: IPsec keeps the internet tidy, reliable, and ready for business (and binge‑watching). It’s the unsung guardian we all rely on, and it’s doing a bang‑on‑the‑front‑shelf job of keeping us safe.
What are the different modes of Internet Protocol Security?
IPSec Unplugged: A Light‑Hearted Guide to Transport & Tunnel Modes
Ever heard about Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) and wondered why it’s such a buzzword? Think of it as the bouncer that keeps data safe while it swings through the digital club. There are two sneaky ways it does its job – Transport and Tunnel. Let’s break it down without the corporate jargon and sprinkle a little humor along the way.
Transport Mode – “Just A Touch-Up”
- What it does: Adds a security “cloak” to the payload (the juicy data), leaving the original packet header untouched.
- Why it’s cool: Keeps the outside world (source/layer addresses) visible, so routers still know where to send things.
- Typical use case: Between two hosts speaking directly, like a secure chat between you and your friend.
Picture This
Data = banana; header = green banana peel. Transport mode is like putting a protective film on that banana peel – the peel stays the same, but the banana inside gets extra protection.
Tunnel Mode – “Full‑On Encryption”
- What it does: Wraps the entire original packet (header + payload) inside a new, encrypted shell.
- Why it’s neat: The old header becomes invisible to intermediate routers; everyone sees only the new header.
- Typical use case: Connecting two networks over a public internet (think a private VPN between offices).
How It Movies Out
Original packet = secret recipe; new header + encryption = child‑proof wrapper. Tunnel mode is like sending your recipe in a locked box – no one outside the box can peek.
Choosing the Right Mode – A Quick Decision Guide
- If you’ve got a direct line-to-line talk, go Transport.
- Need a full‑blown shield over a public Wi‑Fi stretch? Pick Tunnel.
- Want a hybrid? Mix modes, but don’t expect them to talk to each other without a little lingo.
Common Pitfalls (and How to Avoid Them)
- Mislabeling: Mixing up modes leads to “address not found” errors. Keep your mode on the label.
- Configuration drift: One side uses Transport, the other Tunnel – nobody talks, nobody gets data.
- Version confusion: IPsec exists in AX.25, IPv4, and IPv6 flavors. Make sure both ends speak the same dialect.
Take‑away Snippets
- Transport mode = “I just need a cloak.”
- Tunnel mode = “I’d like the whole package sealed.”
- Both modes keep your data from prying eyes, but they act like light vs. heavy armor.
So next time your network admin talks about IPSec, ask: “Which armor are we choosing today? Light cloak or full body?” The answer will nicely steer how your data travels through the digital world. Stay encrypted, stay funny, and keep those data packets safe!
Transport mode
Transport Mode – Your Own Secret Tunnel
What’s the deal? In IPsec’s transport mode, you get a direct, point‑to‑point connection between two devices – like two friends sharing an exclusive chat room.
The twist? Instead of wrapping the whole message, it adds a special IPsec header right after the normal IP header but before the real data. Think of it as a polite knock‑on‑the‑door that says, “Hey, we’re encrypted, come in safe!”
- • Only the payload gets hardened – the outer IP header stays plain.
- • Easy set‑up because it’s basically a “safety net” for the data that follows.
- • Fast, because there’s no overhead on the outer layer.
In short, transport mode is the lightweight, point‑to‑point “spy link” that lets two endpoints talk securely without fussing over the rest of the network traffic.
Tunnel mode
What a Tunnel Mode is All About
Picture this: two separate networks, like two bustling cities, suddenly finding a secret passageway that keeps all their traffic safe. That’s tunnel mode—a cozy, encrypted hallway between two gateways or routers.
Why It Suits You
- Auth & Encrypt, Always! Both ends brag about locking data in a secure vault before sending it across.
- No Need for Device Patches The end users or their devices don’t have to play the IPsec game. The tunnel handles the heavy lifting.
- Keep It Simple Think of it as a VPN but specifically for network-to-network chats.
So next time you hear about “tunnel mode,” just remember it’s the secret, smooth road that keeps your traffic safe, without everyone having to get extra gear. Stay secure, stay cool.
What are the different key management methods?
Unlocking Secure Connections: The Power of IKE
Frustrated with the tedious manual key juggling? Enter IKE, the Internet Key Exchange Protocol that brings automation to your encryption game.
How IKE Works
IKE relies on the Diffie‑Hellman secret‑shaking dance to generate keys faster than you can say “password.”
Meet IKEv2
Fresh off the production line, IKEv2 simplifies setup, fixes the kinks of its predecessor, and gives you smoother connections than a well‑tuned espresso machine.
Manual vs. Automatic Key Management
- Manual – you wire the keys into both ends of the tunnel yourself. Old‑school, time‑consuming.
- Automatic (IKE) – the protocol swaps secrets under the hood, so you can focus on the big picture.
In short, IKE is the modern wand that transforms security from a chore into a breeze.
What are NAT and IPsec?
When NAT Plays Hide‑and‑Seek with IPsec
Ever tried to make a call with a friend while the phone’s read‑out keeps changing? That’s what happens when a NAT takes a clean IP packet, gives it a new address and a brand‑new source port. For IPsec, that makeover is a disaster.
What’s the Crisis?
- The NAT strips an IP packet of its original “identity” and tags it with a fresh IP address and a different source port.
- IPsec checks every packet’s integrity. If the look‑and‑feel no longer matches the original, it throws a tantrum: “This packet is spoiled!”
- That “spoiled” packet is discarded, and the secure handshake falls apart before it even gets started.
Why It Matters
When the NAT tampers with a packet, the entire privacy maze collapses. Your encrypted tunnel can’t even launch, leaving your data exposed or simply dead.
Fix the Woes: Nasty Tricks That Help
- IPsec Pass‑Through – Let the tunnel sneak through untouched, ignoring the NAT’s meddling.
- NAT Traversal – Teach the traffic to “talk to the NAT” directly; they do a kind of handshake so the packet remains valid.
Bottom Line
Keeping NAT out of the dreaded IPsec cross‑road saves you from a secure connection that never gets a chance to exist. Think of it as a friendly reminder: if the trip’s got a lot of changing lanes, make sure the guardrails feel the same.