Explore PKCS: Definitions, Specifications, and More
PKCS Definition
Public Key Crypto: The Skeleton Crew of Asymmetric Security
What the Heck is PKCS?
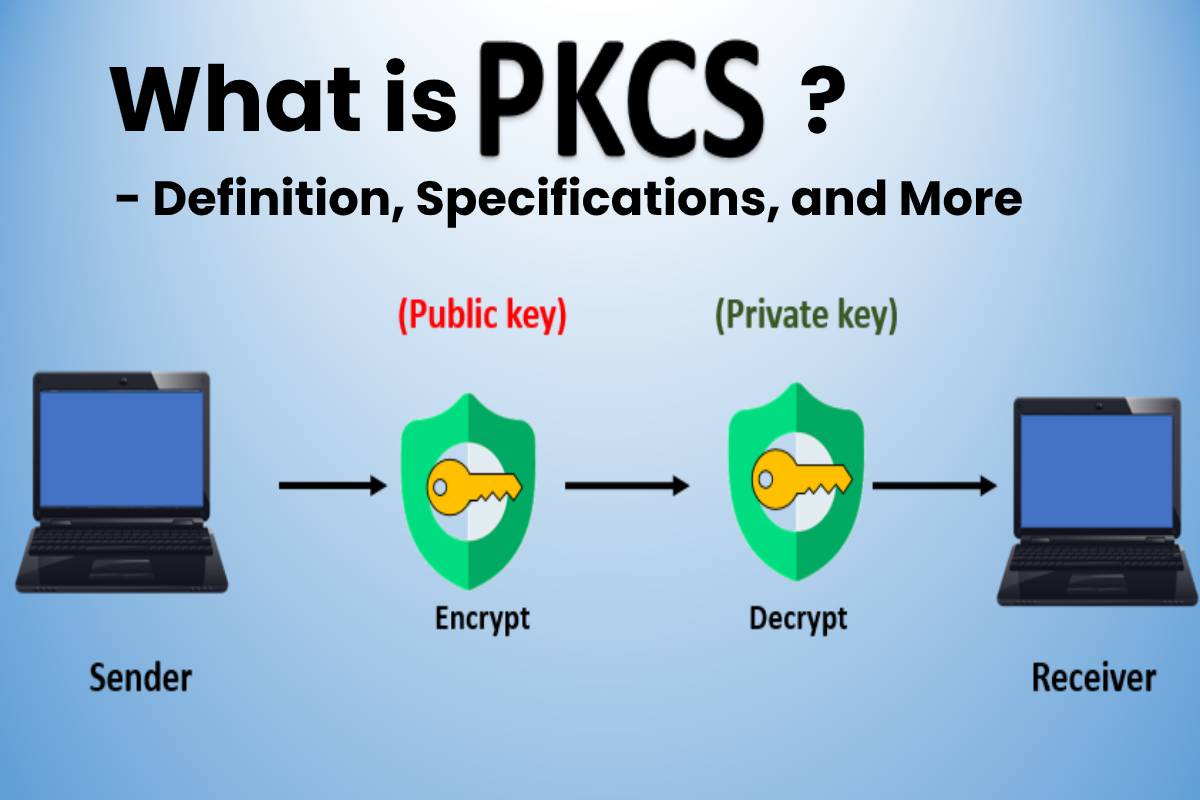
PKCS (short for Public‑Key Cryptography Standards) is basically a grand master plan for the world of asymmetric cryptography. Think of it as the recipe book that tells every digital chef how to whip up a secure dish using public and private keys.
Why Bother With PKCS?
- Spread the Word: It does the heavy lifting to get asymmetric encryption systems everywhere—from your smartphone to the safety‑net of government servers.
- Build Standards: By laying down clear specs, it helps all the wizards in the cryptography playground talk a common language.
- Roll‑out Ready: These standards marry smoothly with IETF partnerships and the PKIX working group, so your encryption is proof‑ready for the real‑world.
The Big Picture
From the moment you hit “Send” to your unsuspecting friend, PKCS rules the roost. It’s a backbone that stitches together different protocols and ensures that whether you’re using RSA, DSA, or anything else, everyone’s on the same wavelength. In short: PKCS is the ultimate playlist for secure asymmetric encryption— no one can hit the wrong chord.
Not Just Fancy Jargon
While the name sounds like court thieves caught in a livery shop (Public Key cryptography sounds like a cryptic nod on a wattle), the real takeaway is simple: PKCS turns complex math into a smooth, everyday security routine. It lets us keep our digital secrets, whether it’s for banking or for the government’s covert ops. The final punchline? It keeps the keys safe, comes with an appropriate collection of standards, and ensures you can pick the right lock without a manual every time.
What are the specifications of PKCS?
How Public‑Key Playbooks Are Taking the Tech World by Storm
Those documents? They’re not just fancy papers; they’re the key to getting everyone on board with the cutting‑edge world of asymmetric encryption—the kind you use when you’re shooting secrets over the internet without anyone tripping over your keys.
What They’re All About
- Spreading the word: They’re designed to push asymmetric encryption into the mainstream and get the tech community to adopt a common set of standards.
- Foundational specs: Think of them as the recipe books that let you bake digital signatures and certificates like a pro chef.
- Standards‑heavy: Several of these docs have already been woven into the fabric of IETF standards, especially the PKIX working group that keeps everything on point.
In short, these documents are the unsung heroes of the internet’s security puzzle—making sure that when you sign a piece of data or set up a certificate, it’s all solid, standardized, and trustworthy.
What are the Public Keys of [PKCS]?
html
Public‑Key Cryptography Standards at a Glance
Ever wondered what all those PKCS acronyms really mean? Below you’ll find a playful snapshot of 15 key areas, each one with a short, breezy description. No heavy jargon—just the essentials you need to get the picture.
1⃣ RSA Procedure
Think of RSA as the “public‑key grandmaster.” It’s the algorithm that lets you sign your data and encrypt it for everyone else—beam it into the future!
2⃣ Diffie‑Hellman Key Exchange
Need a secret handshake? This standard lays down the exact protocol for exchanging keys over a noisy channel, so both sides end up with the same secret without actually sending it.
3⃣ Password‑Based Encryption (PBE)
Here we prove that a password can be turned into a safe, cryptographic key. Think of it as turning your favourite password into a secret sauce for encryption.
4⃣ Extended‑Certificate Syntax
These are the extra goodies attached to certificates—attributes that tell you more than just the owner’s name.
5⃣ Cryptographic Message Syntax (CMS)
CMS is like the Swiss Army knife for encrypted and signed messages. It’s what lets you mix everything from S/MIME to generic secure messaging.
6⃣ Private‑Key Information Syntax
Everything you need to describe a private key, from format to attributes—one neat package that makes keys portable.
7⃣ Certification Request Syntax (CSR)
When you need a certificate, you use a CSR. This standard defines the shape of that request so the authorities know exactly how to process it.
8⃣ Cryptographic Token Interface (CTI)
Also called Cryptoki, this interface standard defines how software talks to hardware tokens—think smart cards or HSMs.
9⃣ Personal Information Exchange Syntax (PINE)
Look‑under‑the‑hood of a portable format that bundles private keys and certificates for easy sharing.
Elliptic Curve Cryptosystem (ECC)
Eccentric curves save space and speed. This standard spells out the parameters that make elliptic‑curve crypto tick.
1⃣ Pseudo‑Random Number Generation (PRNG)
Random is the spice of security. The PRNG standard is still evolving—think of it as a recipe that keeps improving over time.
2⃣ Cryptographic Token Information Format
Just like a résumé for a cryptographic token, this format lists all the attributes and capabilities you need to know.
3⃣ (Missing) – Tossed Out
Some branches of the PKCS family were merged or withdrawn in favour of newer, more robust standards. Think of it as a pruning session to keep the tree healthy.





![Ways IT Industry is Changing the World [2025] Ways IT Industry is Changing the World [2025]](https://www.computertechreviews.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/IT-Industry.jpg)

