Jitter Unveiled: Definition, Functionality, and Key Features
Jitter 101: What the Heck Is It?
Good news, folks! We’ve got a quick, fun guide that demystifies jitter in the world of voice and video tech. Think of it as a traffic report, but for your digital calls. Dive in and find out why your speaker might hiccup, and why fixing it means smoother chats.
Toggling the Definition
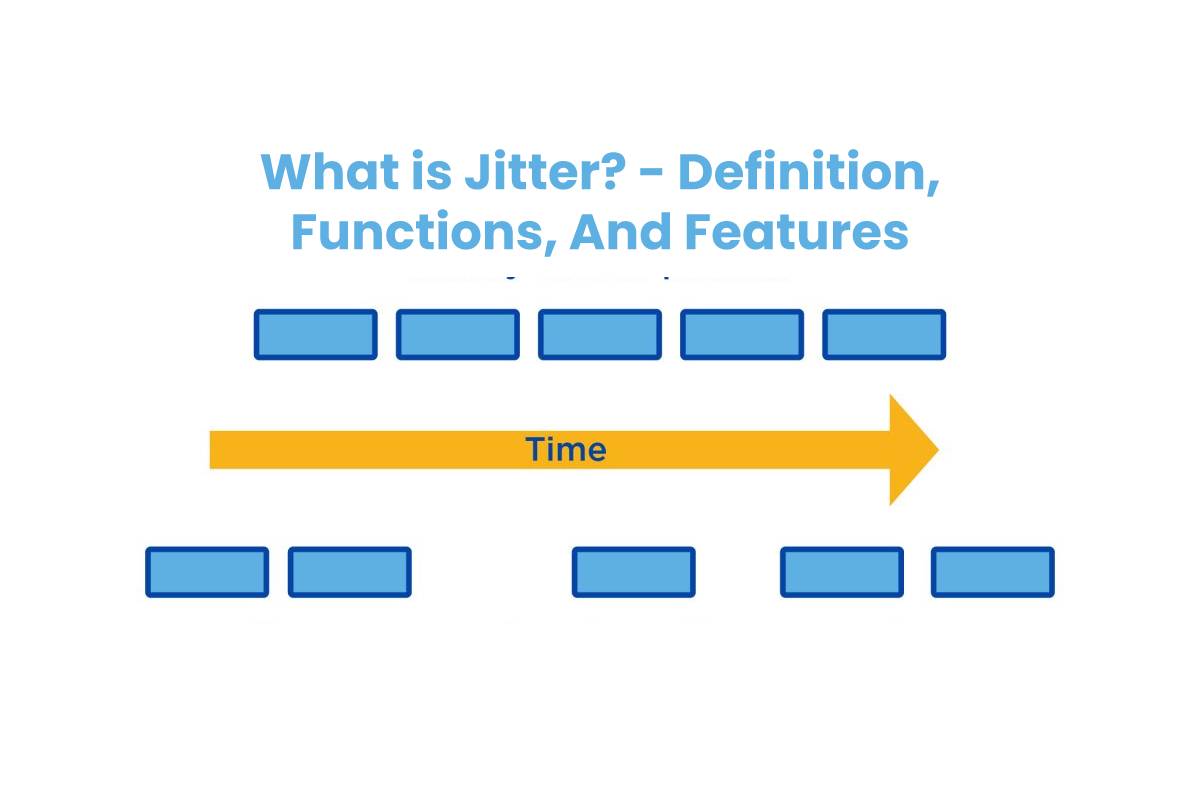
First up, let’s toggle the definition on and off: Jitter is the variation in packet arrival times over a network. In plain English, it’s like those friends who keep arriving in fashionably late or early—unpredictable and a real party‑pooper.
Functionality of Jitter
- Why it Happens: Congestion, routing changes, or even a sudden Wi‑Fi hotspot ‘hiccup’ can bust the rhythm.
- Impact: Music playback pauses, video frames glitch, and voice calls turn into marathons of “Can you hear me?”
Features of Jitter
- Measured in Milliseconds: The lower, the better. A jitter value over 30 ms can start irritating your audience.
- Packet Reordering: Jitter can mix up your data packets—imagine reading a sentence out of order.
- Buffer Athletics: Your device’s buffer tries to smooth out jitter, but it’s like a traffic cop juggling too many cars.
Voice Traffic – The Ultimate Test Subject
Voice packets, being highly time‑sensitive, feel jitter like a hard Saturday night. A quick note: If your call starts sounding like a broken record, it’s probably jitter doing a bad impression of “Irregular Beat.”
Single End Point
One device speaking and one device listening. Jitter here is easier to spot because it’s a single commuter line. If your friend’s call keeps cutting in and out, look for high jitter in that bin.
Double End Point
Now both ends are talking, which doubles the chances of hiccups. Two sides, same problem? That’s a classic case of >30 ms heap‑throw.
Bandwidth Test – The Ultimate Jitter Detective
- Run a speed test to gauge raw bandwidth.
- Run a packet capture while streaming—watch the packet intervals.
- Analyze the jitter histogram—high peaks mean trouble.
Bottom line: low bandwidth equals high jitter. If your Wi‑Fi is crowded like a theme park on peak day, expect jitter spikes. Fixing it means boosting bandwidth or squeezing network traffic.
That’s it, folks! You’ve just hit a 100‑page manual on jitter, one section at a time. Keep your calls smooth and your jokes on point—no more “Can you hear me?” punchlines. Enjoy the upgrade!
Definition Jitter
What the Heck is Jitter?
Ever notice how a video call sometimes hiccups, or your game lags just when you need that big move? That annoying glitch is called jitter—the funky friend that keeps a signal from staying on schedule.
Jitter 101
- Definition: Think of a dance floor with perfectly timed steps. Jitter is when the dancers (or data packets) arrive a tad early or late, messing up the rhythm.
- Where it Happens: Mostly in the world of electronics and telecommunications, especially when a clock signal is the boss.
- Beyond Clock: In networks, we call it packet delay variation. It’s the wobble in the timing of data bursts.
Why Jitter Matters
When packets are meant to travel in a tidy queue, jitter throws a tantrum, shuffling them around like a toddler with crayons.
This scramble leads to:
- Fluctuating delays of milliseconds—sometimes up to 50 ms!
- Network congestion, because every device jostles for the same slice of bandwidth.
- Packet loss: the more chaotic the traffic, the higher the chance that some packets never reach their destination.
Real‑World Consequence
Picture a crowded subway: the gear wars for a seat cause friction. On a network, this friction means your voice call dips, your game lags, or a file download stalls. It’s a subtle reminder that timing matters in the digital realm.
Takeaway
Jitter is the technical version of an erratic drumbeat. Smooth, well‑timed data keeps everything humming. If your networks start to feel offbeat, it might be time to tune the system—or at least play a calmer playlist!
Functionality of Jitter
Jitter: The Unwanted Traffic Jam on the Internet Highway
What It Looks Like on Your Device
Picture your data packets as eager commuters heading to the front door of your computer. Normally they hop from server to server in a smooth relay, like a well‑coordinated flash mob. But when jitter shows up, it’s as if a detour sign tells everyone to line up at a single intersection… all at once. The result? A pile‑up that leaves everyone scrambling.
Why It’s a Bad Party Trick
- Delays, delays, more delays! Your browser waits for the slowest packet, turning a quick 1‑second request into an eternity.
- Data on a treadmill That means the machine on the other side gets a bunch of packets that rush in all together, overwhelming its processing power.
- Lost messages The traffic jam isn’t just slow; it actually causes packets to vanish like socks in a dryer.
When Your End App Gets Crunched
The computer that’s supposed to read the data gets hit by a sudden onslaught. Think of it as a waterfall of junk that spills over the set of seats. It can’t keep up, and the content you expected turns out incomplete or garbled – a real “what do I do now?” moment.
Fixing the Chaos (You Might Not Be a Traffic Cop, but…)
When packet loss is persistent, the receiving device will try to rebuild the lost puzzle pieces. The software essentially goes into “recovery mode,” attempting to re‑establish a smooth flow. Unfortunately, this extra effort is like having to tip over the entire traffic jam just to get one seat back.
In short, jitter is the internet’s version of burnt‑time coffee: it makes everything sluggish and you’re left wondering why you have to wait forever for that one blink of a webpage.
Features of Jitter
When Jitters Turn Into Jests: A Friendly Guide to Network Lag
Ever tuned into a video call that sounds like a broken vinyl record? That’s typical jitter at work—those odd, sporadic delays that make your voice overlap, pause, or fade out. While it’s a nuisance, it doesn’t always spell doom for a smooth conversation.
What Makes a Jitter Taboo?
Network congestion is the villain here. Picture a highway jam: packets rush in, the buffer gets full, and suddenly, some of them are demolished (or dropped). The real killer is when jitter surpasses comfortable limits.
Acceptable Thresholds (Keep ‘Em in Check)
- Packet delay less than 30 ms – Your voice stays snappy.
- Loss below 1% of packets – Nothing feels missing.
- Total latency under 150 ms – The whole call stays swift.
When those numbers hold, jitter is usually just a polite nudge, not a raging storm.
When is Jitter Still the Party Crasher?
Anything beyond 20 ms starts to trip up real‑time talks. Once it crosses 30 ms, folks hear distortion and slow responses. The worse the jitter, the more your messages get fluffed up, confusing listeners.
Why Voice Calls Are the Prime Victim
VoIP is like a game of musical chairs for your words. Your voice splits into tiny packets, hops across the network, and sails to the other end. If those packets arrive jumbled, the rhythm breaks, and everyone feels the hiccup.
Different services react differently: a glitching video call might feel like a glitchy old TV, while a voice call gets the most noticeable wobble. That’s why keeping jitter low is a top priority for any voice-based service.
Bottom Line: Keep Your Jitter in the Desired Range
Think of it like this—gentle “tremor” up to 30 ms, low packet loss, and latency under 150 ms = great communication. Aim higher for 20 ms for the best experience, especially if you’re on a live call. Stay tuned, stay cool, and let the network flow smooth as you talk the talk!
Voice traffic
How Control Over Endpoints Gets the Doctor’s Nod
Why This Matters
In the world of software, the measure that matters most revolves around whether a user has wrenches in just one toolbox or in both. Imagine playing a game of policy control—the fewer knobs you touch, the more predictable the results.
The Two Scenarios
- Single EndPoint Control: You’re the master of one point in the network. This gives you a laser‑focused influence, but you’re also exposed to any hiccups that happen there.
- Dual EndPoint Control: You hold the reins of both points, which feels like a superhero cape. You can x‑ray the entire system, but the risk of a double blunder is higher.
What It Looks Like in Practice
Picture a developer who can toggle features on a single service—easy to test, easy to rollback. Now crank it up to both services, and you’ve got a full‑stack debugging wizard. But keep in mind that every extra toggle introduces a fresh point of failure.
In short, the rate‑measuring metric is basically: Does the user have a solo cheat code or a dual‑target master switch? Tailoring your control design around this triage keeps the system both robust and managable.
Single End Point
Crunching Voice Packet Latency
Ever wondered how your voice call feels instant or sluggish? It all comes down to a couple of quick checks on your network’s heartbeat. We look at two key numbers:
- Average Round‑Trip Time (RTT) – gives a snapshot of the typical delay between sending a voice packet and getting a reply back.
- Minimum Round‑Trip Time – shows the best‑case latency, the sweet spot where packets flow like a well‑tuned conversation.
By sampling a handful of voice packets, we can capture these stats and get a clearer picture of how smooth or lag‑prone your call will be.
Double End Point
Getting a Sense of Jitter
Picture a line of packages being sent across a network. If each package arrives exactly on schedule, everything runs smoothly. But when the timing starts to wobble—some arrive early, some late—those irregular gaps are what we call jitter.
How We Measure It
The gold‑standard way to gauge jitter is by looking at the instantaneous jitter—the tiny fluctuation between the moment a packet leaves the sender and the moment it lands on the receiver.
- Instantaneous Jitter: Snapshots of timing differences gathered on a packet‑by‑packet basis.
- Transmission‑to‐Reception Gap: The overall variance in intervals from when a packet is sent to when it’s received.
In short, it’s all about watching how the gaps between packet intervals dance around—any wobble signals that the network might be having a bad day.
Bandwidth test
Why Bandwidth Tests Outshine Math for Spotting Jitter
Think you can calculate the wobble in your network with a calculator? Think again.
The Smart Move: Hit the NIBBLE
When your data is hopping around like a jittery frog, the quickest way to gauge how much it’s bouncing is to actually run a bandwidth test. No heavy math, no confusing formulas—just plug in a simple check and let the numbers do the talking.
How It Works
- Run a test that measures your current data speed.
- Compare the reading against the ideal rate.
- A significant drop means your jitter is in full swing.
Pro Tip: Keep It Simple
Never forget, the simplest tool is often the best. Instead of drowning in equations, just let your network speak for itself with a quick bandwidth test.







